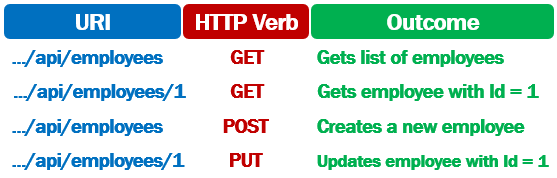
To update an existing item, issue an HTTP PUT request to the URI /api/employees/ID. The ID of the employee to update must be passed in the URI.
ASP.NET Core REST API - HTTP PUT Example
Code Explanation
It is the PUT request that is used to update an existing employee. This is the reason UpdateEmployee() method is decorated with the HttpPut attribute.
EmployeesController class is decorated with ApiController attribute. This attribute allows the data from the request to be mapped to the employee parameter on UpdateEmployee() method.
Either this ApiController attribute is required or the method parameter must be decorated with [FromBody] attribute. Otherwise, model binding will not work as expected and the employee data from the request will not be mapped to the employee parameter on the UpdateEmployee method.
HttpPut attribute on UpdateEmployee() method also has a route template. The id of the employee will be appended to the URL /api/employees. So the URL becomes /api/employees/5
The employee id value in the URL is automatically mapped to the id parameter on the UpdateEmployee(int id, Employee employee) method.
As we are using the int route constraint on the id route parameter, the id value in the URL is mapped to the method parameter, only if the value is an integer.
Complete EmployeeController Code
using EmployeeManagement.Api.Models; using EmployeeManagement.Models; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc; using System; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace EmployeeManagement.Api.Controllers { [Route("api/[controller]")] [ApiController] public class EmployeesController : ControllerBase { private readonly IEmployeeRepository employeeRepository; public EmployeesController(IEmployeeRepository employeeRepository) { this.employeeRepository = employeeRepository; } [HttpGet] public async Task<ActionResult> GetEmployees() { try { return Ok(await employeeRepository.GetEmployees()); } catch (Exception) { return StatusCode(StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError, "Error retrieving data from the database"); } } [HttpGet("{id:int}")] public async Task<ActionResult<Employee>> GetEmployee(int id) { try { var result = await employeeRepository.GetEmployee(id); if (result == null) { return NotFound(); } return result; } catch (Exception) { return StatusCode(StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError, "Error retrieving data from the database"); } } [HttpPost] public async Task<ActionResult<Employee>> CreateEmployee(Employee employee) { try { if (employee == null) { return BadRequest(); } var emp = employeeRepository.GetEmployeeByEmail(employee.Email); if (emp != null) { ModelState.AddModelError("email", "Employee email already in use"); return BadRequest(ModelState); } var createdEmployee = await employeeRepository.AddEmployee(employee); return CreatedAtAction(nameof(GetEmployee), new { id = createdEmployee.EmployeeId }, createdEmployee); } catch (Exception) { return StatusCode(StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError, "Error creating employee"); } } [HttpPut("{id}")] public async Task<ActionResult<Employee>> UpdateEmployee(int id, Employee employee) { try { if (id != employee.EmployeeId) return BadRequest("Employee ID mismatch"); var employeeToUpdate = await employeeRepository.GetEmployee(id); if (employeeToUpdate == null) return NotFound($"Employee with Id = {id} not found"); return await employeeRepository.UpdateEmployee(employee); } catch (Exception) { return StatusCode(StatusCodes.Status500InternalServerError, "Error updating data"); } } } }
No comments:
Post a Comment